Solid State Drives (SSD), Hard Disk Drives (HDD), and Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) are three types of disk technologies that serve different storage needs. Each type has unique characteristics, advantages, and use cases, making them suitable for different environments and applications.
Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
HDDs are the oldest and most traditional form of storage technology. They use spinning platters and read/write heads to access data, making them a mechanical and magnetic storage medium. HDDs are cost-effective and offer large storage capacities, which makes them ideal for data archiving and applications that require a lot of storage without needing very high speeds.
- Pros: Cost-effective, large capacity, widely available.
- Cons: Slower speed compared to SSDs and NVMe, mechanical parts prone to wear and tear.
Solid State Drives (SSD)
SSDs use NAND-based flash memory to store data, which provides significantly faster data access speeds compared to HDDs. SSDs have no moving parts, making them more durable and energy-efficient. They are commonly used for operating systems, applications, and other tasks where fast access times are critical.
- Pros: Faster read/write speeds, more durable, energy-efficient.
- Cons: More expensive per GB compared to HDDs, limited write cycles (though less of an issue with modern SSDs).
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe)
NVMe is a protocol that allows SSDs to connect directly to the computer's PCIe bus, resulting in even faster data access compared to traditional SATA SSDs. NVMe drives provide low latency and high throughput, making them perfect for high-performance computing, gaming, and workloads that demand the fastest data access possible.
- Pros: Extremely fast data access, low latency, ideal for performance-intensive tasks.
- Cons: Higher cost compared to SATA SSDs and HDDs, may require specific motherboard support.
Comparison Summary
- HDD: Best for cost-effective, high-capacity storage where speed is not a priority.
- SSD: Ideal for fast performance, reliability, and energy efficiency for everyday computing and applications.
- NVMe: Suited for power users, gaming, and environments needing the highest speed and lowest latency.
Choosing between HDD, SSD, and NVMe depends on your specific needs, budget, and performance requirements. For large storage at a low cost, HDD is a good choice. For a balance of speed and cost, SSD is suitable, while NVMe is ideal for those who require top-tier performance.
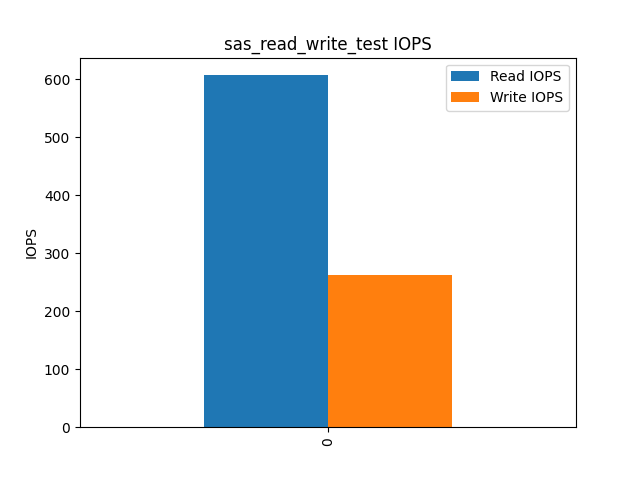
Apart from the native benefits of each disk technology, the local use cases also play a significant role in choosing between HDD, SSD, and NVMe.
The SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) drives also offer good performance, but as evident from the graph, their IOPS are significantly lower compared to NVMe drives, especially in read operations.
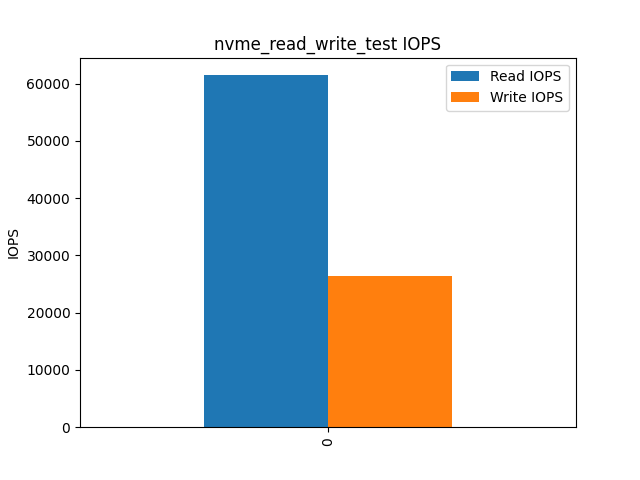
The above graph shows the IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) for NVMe disks during read and write tests. NVMe drives provide substantially higher IOPS compared to other disk technologies, making them ideal for applications requiring high-speed data transfer.
The world of storage technologies—HDD, SSD, and NVMe—promises to be an exciting mix of performance, capacity, and cost-effectiveness, catering to different user needs and environments.